AI Agent Governance: What to Prepare for as AI Enters Your Stack
AI agents are here, and they’re not just suggesting actions. They are taking actions as well, on their own! The question is: who’s governing them?

This article is part of the short series. Part I. deals with demonstrating the strengths of Superset and how it’s situated in the diverse dataviz market, while the upcoming Part II. will discuss our experience in implementing and testing Superset on the pipeline illustrated with the figure below.
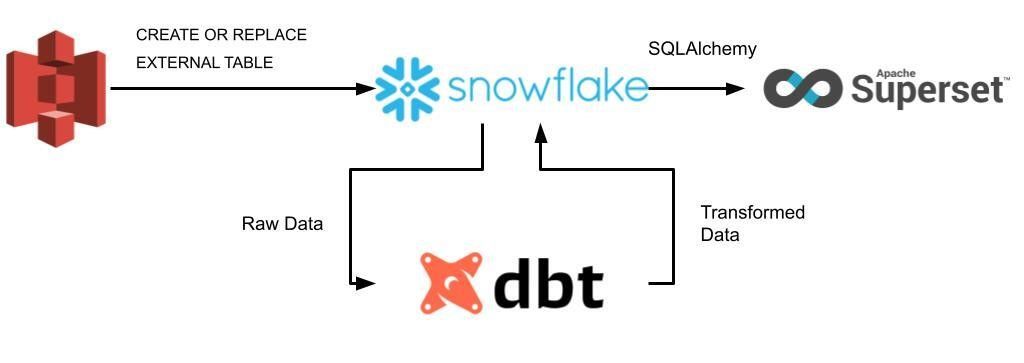
When we talk about interactive data visualization, especially in the context of modern data stacks (e.g. data streamer (Stitch, Fivetran, Airbyte) + centralized cloud storage (AWS, Azure, GCP, Snowflake, Databricks) + transformation tool (dbt) + BI platforms), proprietary tools pop into our head such as Tableau, Power BI, and more recently Looker. These were considered as the mainstream solutions for quite a while, but now, emerging open-source alternatives are hungry enough to beat the market with their simplicity and cost-friendly approach. Among these promising technologies, Apache Superset is set to challenge its competitors in many ways, therefore, Hiflylabs closely monitors the roadmap of the project.
Given the maturity and dynamism of the BI market, consolidations are more frequent than ever. Over the past few years, other commercial tools were acquired by companies such as Tableau by Salesforce, Looker by Google Cloud, or Periscope by Sisense, which can infer the risk of vendor lock-ins forcing customers to migrate and rebuild their assets (e.g. Chart.io was downsized and shut down by Atlassian). Conversely, open-source platforms such as Superset avoid vendor lock-ins since you can both switch between commercial open source (COSS) vendors, and host it yourself on-premise. A good example for the former would be Preset (founded by the creator of Superset, Max Beauchemin), who offers a hassle-free and fully-managed cloud SaaS service to the platform.
Well, as the name indicates, Superset started in the Apache incubator back in 2016 and quickly became one of its top priority projects coinciding with the recent stable release at the beginning of 2021. It’s a modern, lightweight, cloud-native, free, and open-source BI web application with an advantageous SQLAlchemy python backend, making it scalable and compatible with almost any database technology speaking SQL. To reflect its increasing popularity, Airbnb, Twitter, Netflix, Amex, and many other companies have already started incubating Superset in their workflows, while Dropbox managed to successfully exploit its advantages at an enterprise level. In addition, the growing community behind Superset further strengthens the argument that there is an undeniable potential in our sight.
Superset essentially stands on three main layers:
We have seen many instances for pairing Looker with dbt, but the following arguments made us advocate for Superset:
Let’s see a case study on how Superset was chosen to be implemented into enterprise-level production!
The table below was retrieved from a Dropbox article on Jan 19, 2021. Long story short, they desired to find one particular BI tool to replace multiple other solutions. The main emphasis was on the security, user-friendliness, maintainability, flexibility, and extensibility of the platform. Their choice also landed on Superset as it was the best match for their specific internal needs. As a part of their decision-making process, they provided a comparison table that shows that Superset is superior compared to its peers in terms of the number of features and compatibility.
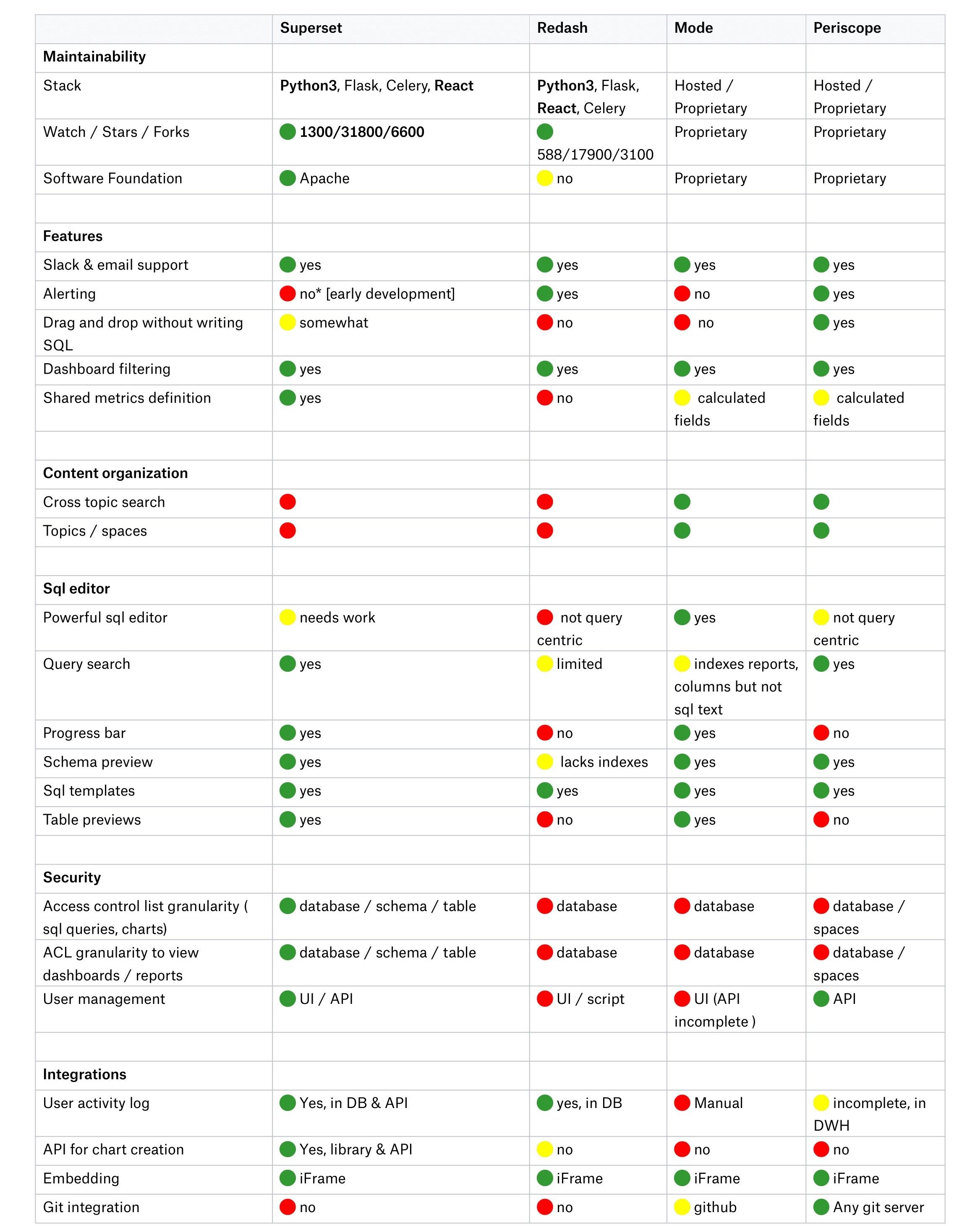
Dropbox explained ditching Metabase with the argument that it's developed in Clojure rather than Python, while to their knowledge, it has shortcomings from many additional aspects compared to Superset, for example, it has less authentication and data backend support. Since Dropbox has many strong Python developers, they decided to pursue Superset instead of Metabase.
Just as other tools, Superset also has its limitations.
Did Superset spark some interest in you or it still falls short of being a credible solution to your pipeline? What are the missing features which would elevate the product to a day-to-day alternative for you? Make sure that your voice is heard in the comment section below! Also, stay tuned for the second part of the series!
Son N. Nguyen - Data Engineer
The founders of Hiflylabs have made their name by offering risk analysis and fraud detection for various financial institutions long before machine learning even became a buzzword.
With this new wave of AI, our opportunities have multiplied.
Banking, insurance, legal, M&A, private equity, investors and fintech players are all winners in this round.
Risk assessment for deals, evaluating company performance for potential investors, identifying anomalies in business records, or streamlining routine tasks are all made easier by the process automation offered by agentic AI ensembles.
Financial Times has even published an article titled “Automation is coming for private equity’s junior roles”!
And as for customer experience, QoL changes for fintech users are happening across the board. For example, our latest integration has resulted in 10x less administrative load for fintech users!
Retail and consumer packaged goods benefit from real-time analysis and insights the most.
Dynamic pricing and inventory optimization can not only result in a competitive edge, but also increase the sustainability of your operations in a tangible way. Identifying and predicting seasonal shifts in customer demand for certain products, and following customer behavior real-time will decrease your wastage—resulting in less pollutants heading into landfills and the environment
Optimizing your inventories and offerings, automating analytics subtasks and tailoring customer experience to their needs makes for a more profitable business.
Artificial Intelligence at large will revolutionize robotic surgeries, drug discovery, longevity research and more.
But the short run will be all about assisting doctors in making more informed decisions by synthesizing all the unstructured data available in patient records in ways that just weren’t possible before.
Personalization and predictive diagnostics will be the most important advances generative AI brings to the table right now.
While AI regulations are just rolling in, the sector is already subject to some of the strictest policies regarding personal data security, which are about to tighten even further. As such, healthcare institutions need unified AI governance.
The operational challenge here is creating customized solutions that are on par with state-of-the-art products, and setting up streaming data workloads & AI personalization in isolated ecosystems.
We are currently neck-deep in multiple healthcare prospects, so we shan’t say any more for now—an upcoming post will be dedicated to the scope of these initiatives.
If you have an assembly line, then supply chain optimization, quality control and automation are your obvious top AI use cases.
To be more specific, running simulations to find defects, setting alerts for predictive maintenance, or evaluating production models by an automated framework will boost your bottom line by saving you both time and costs.
The analytical / business side of entertainment couldn’t be sunnier. Churn prevention is easier than ever, as real-time analytics can now be augmented by automated alerting and personalized outreach processes.
However, the long-run is a looming mountain of generated content. We are still at the very beginning of this paradigm shift, but ultimate levels of personalization in every possible multimedia format is coming our way. The silver lining will be compute getting cheaper and consuming less energy as time goes on.
Telco prioritizes streaming workloads as an infrastructure priority, with quick adoption of emerging tech following close.
For residential services, the increasing automation of customer support and related quality control are finally technologically mature enough to feel useful. Chatbots are often people's first encounter with business AI, but historically these bots have struggled with complexity. Now, AI agents can even take actions on human customer support representatives’ behalf.
We’re also seeing the rise of real-time, automated translations which will have a global impact on all communication.
Furthermore, AI embedded into communication infrastructures is increasingly able to predict system issues and dynamically allocate resources for more reliable service.
AI automation revolutionizes the energy industry through predictive modeling, optimizing distribution and consumption while enhancing grid security.
Anomaly detection was already a use case with incredible ROI in this sector, further optimizing such systems with agentic decision making is poised to generate even greater value.
The international energy market is a huge opportunity as well, as its sole reliance on predictive analytics makes it a prime candidate for agentic process optimization. Real-time trading, dynamic grid management, risk assessment, price and demand forecasting are all being utilized right now, and are immediate beneficiaries of further fine-tuning by AI.
Industry still dominates AI research—their results dwarf universities or government agencies.
The public sector is trying to catch up globally, with some countries being more successful than others.
Furthermore, all eyes are on policymakers who are left with figuring out governance.
Having said that, the states’ AI use cases are plenty and promising: predictive maintenance of public properties, real-time analytics of important data for timely intervention, public education reforms with revolutionary personalization, and overall process automation—all great prospects for the future.
The US government has recently made their top current AI use cases public. The Department of Energy is leveraging AI the most by far, followed by Health and Human Services, Commerce, and Homeland Security respectively.
And now, let’s zoom out again.
Looking beyond current applications, several factors could shape AI's trajectory.
We are aware that rapid technological progress can radically shift the course we all will take.
Here are some dynamics we can forecast relatively safely:
People across all industries are more cognizant of AI’s potential impact—but the use cases and technical solutions that carry the most value can continue to elude people as tech advances are happening faster than most organizations are used to responding.
2024 is the year of AI agents. Will 2025 be about them still? We can only expect the unexpected, and prepare for the next step of evolution.
You have to be ready to dramatically accelerate the democratization of data and AI in the enterprise, and incorporate today’s solutions into a unified data intelligence foundation.
Only those ready for continuous adaptation will achieve future-proof scalability and robustness, and strike real gold with AI.